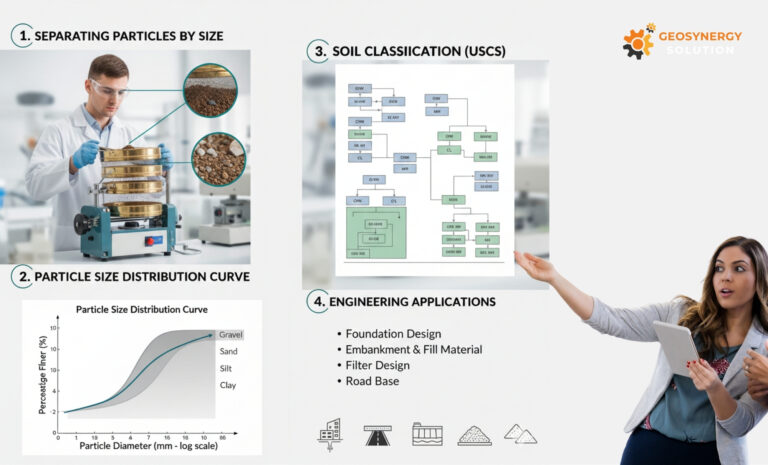
Why Sieve Analysis Is Important in Soil Classification
Sieve analysis is one of the most essential laboratory tests used in soil classification. It determines how soil particles are distributed based on their size. Because soil behavior strongly depends on grain size, sieve analysis provides the foundation for identifying soil types, predicting engineering performance, and supporting design decisions in construction, mining, and geotechnical projects.
Furthermore, this method helps engineers understand whether a soil is suitable for foundations, embankments, road structures, or drainage layers. With accurate particle-size data, risks such as settlement, instability, and poor compaction can be significantly reduced.
What Is Sieve Analysis?
Sieve analysis is a laboratory procedure used to separate soil into different particle-size ranges using a stack of sieves. Each sieve has a specific opening size, allowing engineers to determine how much material passes through or is retained at each layer. As a result, this process provides a clear overview of soil gradation.
Artikel terkait: Specific Gravity: Key Parameter in Soil and Geotechnical Engineering
Why Sieve Analysis Matters in Soil Classification
1. Identifies Soil Type Accurately
Sieve analysis allows engineers to classify whether a soil is gravel, sand, silt, or a mixture of different fractions. Soil classification systems such as USCS, AASHTO, and SNI rely on particle-size distribution to determine soil groups.
2. Predicts Engineering Behavior
Because different grain sizes behave differently, sieve analysis provides essential data to predict:
Compaction characteristics
Drainage capability
Bearing capacity
Settlement potential
Strength and stability
Consequently, this helps engineers choose the correct construction method.
3. Improves Construction Quality and Safety
Sieve analysis ensures that soils used in foundations, roadbeds, or embankments meet required specifications. Proper gradation reduces construction failures and ensures stable, long-lasting structures.
4. Supports Material Selection for Engineering Projects
Construction materials such as aggregates, sand bedding, and filter layers must meet specific grain-size criteria. Sieve analysis ensures that selected materials meet design standards.
5. Reduces Project Risks
With reliable particle-size data, engineers can:
Avoid weak foundation soils
Prevent excessive settlement
Improve compaction results
Ensure proper drainage performance
Therefore, sieve analysis plays a critical role in minimizing design and construction risks.
How Sieve Analysis Supports Soil Classification Standards
Soil classification systems use sieve analysis to determine:
Percentage passing through each sieve
Gradation curve
Soil group symbols
Engineering properties associated with soil type
For example, sands with well-graded distributions are typically stronger and more stable compared to uniformly graded soils. This information is crucial in engineering decision-making.
Sieve analysis is essential in soil classification because it provides the fundamental data needed to understand soil behavior, select suitable materials, and design safe engineering structures. With accurate gradation information, engineers can make informed decisions and reduce the risk of construction failures.
For these reasons, sieve analysis remains one of the most important tests in geotechnical engineering.

